Seamless Data Migration: From SAP to BigQuery
In the dynamic landscape of data management, the migration of data from one platform to another is a strategic move that organizations often undertake to enhance their analytics capabilities and optimize their data infrastructure. One such migration path is from SAP to Google BigQuery, two powerful platforms that can shape the way businesses handle and analyze their data. In this article, we explore the process of migrating from SAP to BigQuery and highlight the benefits of making this transition.
Understanding SAP and BigQuery
SAP is a well-known enterprise resource
planning (ERP) system that integrates various business processes into a single
unified system. It plays a pivotal role in managing financials, operations,
human resources, and more, providing organizations with a comprehensive view of
their business processes.
Google BigQuery, on the other hand, is a
cloud-based data warehousing solution designed for analyzing vast amounts of
data quickly and efficiently. It offers scalable and flexible data storage and
processing capabilities, making it an attractive choice for organizations
seeking to harness the power of big data analytics.
The Migration Process
Migrating from SAP to BigQuery involves several
key steps:
Assessment: The first step is to assess the
existing SAP environment. This involves understanding the data schema, data
types, and volume of data. It's crucial to identify any data transformation or
mapping that may be required during the migration process.
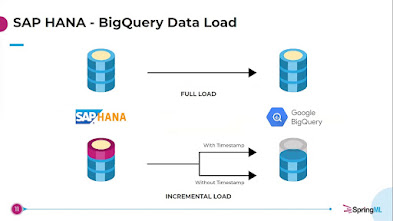
Data Extraction: Data extraction from SAP
systems can be complex, as these systems often contain intricate data
structures. Depending on the data extraction method chosen, this step might
involve using SAP-specific tools or third-party integration platforms.
Data Transformation: During this phase, the
extracted data is transformed to match the schema and format required by
BigQuery. Data cleansing, mapping, and conversion take place to ensure that the
data is accurate and consistent.
Data Loading: The transformed data is
loaded into BigQuery. This can be achieved using Google Cloud's data transfer
services, such as Google Cloud Storage or Google Cloud Dataflow, ensuring a
smooth and efficient data loading process.
Testing: Rigorous testing is essential to
verify the accuracy of the migrated data. It involves comparing the data in
BigQuery with the source SAP system to ensure that the migration was
successful.
Validation: After data loading and testing,
it's important to validate the data in BigQuery to ensure that it meets the
expected standards of quality and accuracy.
Benefits of Migrating to BigQuery
Scalability: BigQuery's architecture allows
organizations to scale up or down based on their data processing needs. This
flexibility ensures optimal performance regardless of the data volume.
Speed: BigQuery's distributed computing
approach enables lightning-fast queries, even when dealing with massive
datasets. This speed enhances the efficiency of data analysis and reporting.
Cost Efficiency: With a pay-as-you-go
pricing model, BigQuery offers cost efficiency. Organizations pay only for the
resources they use, making it a cost-effective solution.
Integration: BigQuery seamlessly integrates
with other Google Cloud services, such as Google Data Studio and Google Sheets,
allowing for a cohesive data analysis ecosystem.
Advanced Analytics: BigQuery supports
advanced analytics, including machine learning and AI capabilities, enabling
organizations to extract deeper insights from their data.
Security: Google Cloud employs robust
security measures, ensuring that data is stored and processed with high levels
of security and compliance.
Considerations and Challenges
While the benefits of migrating from SAP to
BigQuery are substantial, there are also considerations and challenges to be
aware of:
Data Complexity: SAP systems often have
complex data structures that may require intricate transformation during
migration.
Data Mapping: Mapping data from SAP fields
to corresponding fields in BigQuery might require careful planning and mapping
rules.
Data Volume: Managing large volumes of data
during extraction, transformation, and loading can be resource-intensive.
Data Consistency: Ensuring data consistency between the source SAP system and BigQuery requires thorough testing and validation.
The migration from SAP to Google BigQuery
presents a strategic opportunity for organizations to unlock the potential of
advanced data analytics, scalability, and cost efficiency. By seamlessly transferring
data from an established ERP system to a cutting-edge cloud-based data
warehousing solution, organizations can enhance their decision-making processes
and gain a competitive edge in their industry.
However, this migration is not without its
challenges. The complexity of SAP systems and the need for accurate data
mapping and transformation demand careful planning and execution. Engaging with
experienced professionals or third-party experts can streamline the migration
process and ensure a successful transition.
In the evolving landscape of data
management, the migration from SAP to BigQuery can mark a significant step
forward for organizations looking to harness the power of modern data analytics
platforms. With thorough planning, meticulous execution, and a commitment to
data quality, businesses can embrace this migration as a pathway to more
efficient data utilization and informed decision-making.
.jpg)


Comments
Post a Comment