The Working of the Snowflake Data Lake
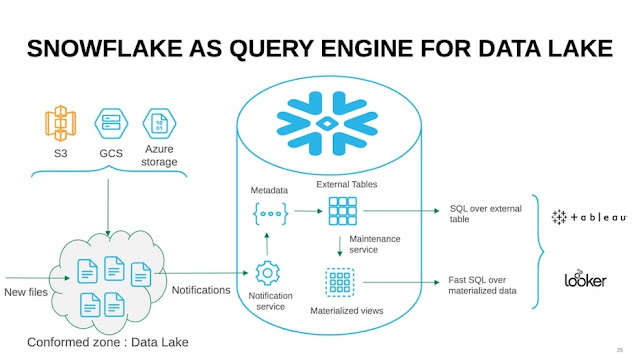
A data lake is a storage repository that is highly scalable and flexible and holds massive volumes of data. Further, data lakes can hold data in its native format, whether unstructured, semi-structured, or structured. Thus, organizations that need to store huge volumes of data in any form prefer data lakes. Snowflake, a fully secured and high-performing platform, has all the attributes of both a data warehouse and a data lake, and hence, businesses prefer the Snowflake data lake as their main data storage system. The Snowflake data warehouse function can be used for storing data in AWS S3, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Storage and make data analytics and data transformation faster. There are several benefits of the Snowflake Data Lake. It can hold data in any format along with structured data such as CSV, Parquet, JSON, and tables. It has high computing powers and the performance of the Data Lake is not impacted even when multiple users simultaneously execute multiple querie...




